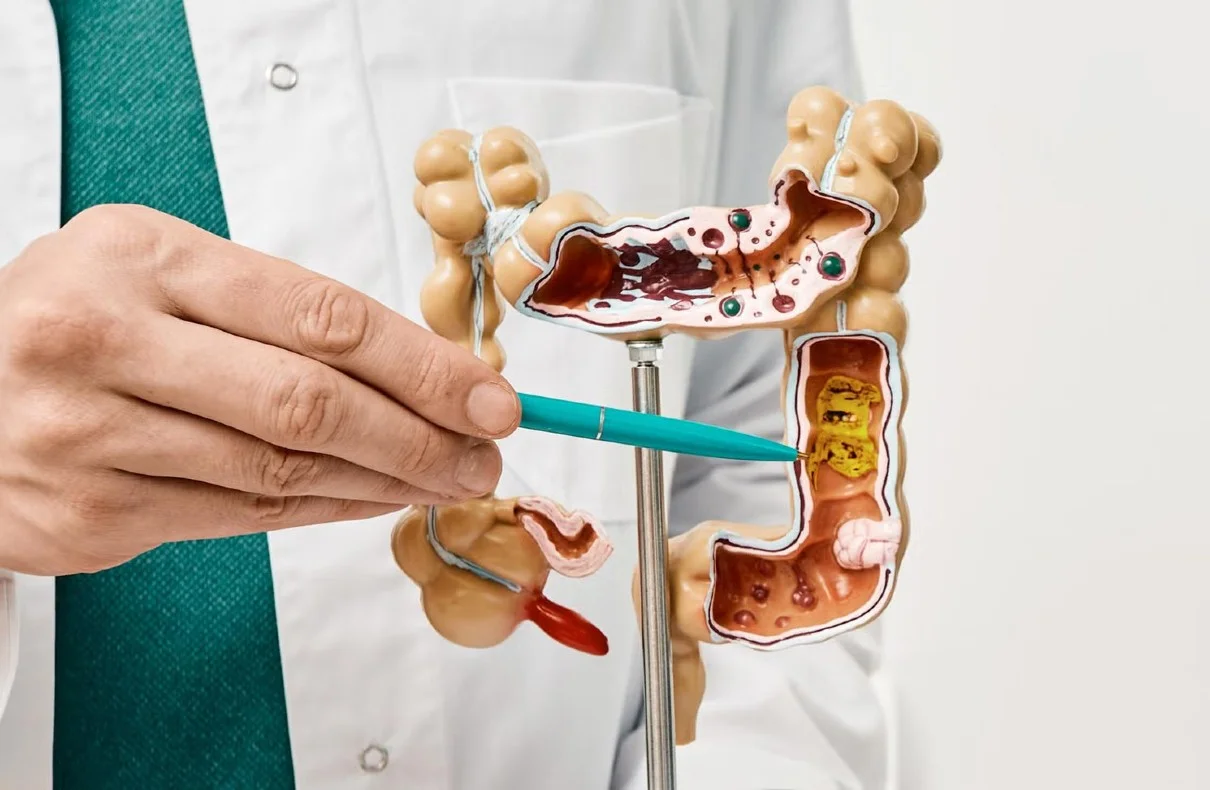
Colon cancer, also known as colorectal cancer, has become a growing concern among younger adults in recent years. This alarming trend has led to an increase in diagnoses and deaths from the disease in this age group. The rise in colon cancer cases among younger generations has puzzled researchers, as the causes and risk factors for this increase are still not fully understood.
Colorectal cancer encompasses both colon and rectal cancer. It occurs when cells in the colon or rectum grow uncontrollably, forming abnormal growths called polyps that can develop into cancer over time. According to the American Cancer Society, the risk of developing colorectal cancer is approximately 1 in 23 for men and 1 in 25 for women. Genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors can influence an individual’s risk for colorectal cancer.
The statistics surrounding colon cancer in younger adults are concerning. The American Cancer Society reports that the proportion of colorectal cancer cases in people under the age of 55 has doubled from 11% in 1995 to 20% in 2019. In fact, individuals born after 1990 are twice as likely to be diagnosed with colon cancer and four times more likely to develop rectal cancer compared to those born in 1950. Moreover, the rate of advanced-stage diagnoses has been rapidly increasing, reaching 60% in 2019.
The exact reasons behind the rise in colon cancer cases among younger generations are still unclear. While lifestyle factors such as obesity, sedentary behavior, and poor dietary choices have been identified as potential contributors, they alone cannot account for the significant increase in diagnoses. Researchers believe that there may be a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental factors at play. Additionally, certain ethnic groups, including Alaska Natives, Native Americans, and Black Americans, have higher rates of colorectal cancer diagnoses.
Environmental factors, including exposure to pollutants, chemicals, and toxins, have also been under scrutiny as potential causes of colon cancer in younger adults. Studies have shown a correlation between air and water pollution, pesticide use, and increased colorectal cancer risk. The National Toxicology Program has identified chemicals that can induce colorectal cancer in animal models, suggesting a potential link between environmental toxins and the disease. However, more research is needed to establish a definitive connection.
Syphilis Epidemic Sweeps Across the US
Diet plays a crucial role in colorectal cancer risk, and the modern Western diet, high in processed foods and low in fruits and vegetables, has been associated with a higher likelihood of developing the disease. However, it’s worth noting that healthy lifestyle choices do not completely eliminate the risk, as many young patients diagnosed with colon cancer lead healthy lives.
Another area of research is the role of the gut microbiome in colorectal cancer. The gut microbiome is a collection of bacteria that reside in the digestive tract and play a crucial role in maintaining overall health. Disruption in the balance of gut bacteria due to dietary choices, antibiotic use, and other factors may contribute to the development of colorectal cancer. Inflammation, triggered by an unhealthy diet and imbalanced gut microbiome, has also been linked to an increased risk of developing colon cancer.
Early detection is key in improving outcomes for individuals with colorectal cancer. The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force modified their recommendations in 2021, lowering the age for colon cancer screening from 50 to 45 due to the rise in cases among younger adults. However, the majority of cases diagnosed in individuals under 55 are already at an advanced stage, making effective treatment more challenging.
Screening methods such as colonoscopy, which allows for the direct inspection of the colon and removal of polyps, remain the gold standard for detecting colorectal cancer. Other screening tests, such as checking for cancer DNA or blood in the stool, may be appropriate for certain patients. It is crucial for individuals to discuss their risk factors and screening options with their healthcare providers to determine the best course of action.
Being aware of the early signs and symptoms of colorectal cancer is crucial for prompt medical attention. Some common symptoms include changes in bowel habits, blood in the stool, unexplained weight loss, abdominal pain, and fatigue. It is important to note that these symptoms may resemble other conditions, and individuals should not delay seeking medical advice if they experience persistent or concerning symptoms.
Why Colon Cancer is on the Rise in Young Adults
One significant challenge in combating colon cancer among younger generations is raising awareness. Many young adults are not aware that they can develop colorectal cancer, leading to delayed diagnoses and missed opportunities for early intervention. Efforts to educate the public about the rising incidence of colon cancer in younger adults and the importance of screening and healthy lifestyle choices are crucial in addressing this knowledge gap.
To better understand the causes and risk factors associated with colon cancer in younger adults, further research is needed. Collaborative efforts between researchers, healthcare professionals, and policymakers are essential in identifying environmental, genetic, and lifestyle factors that contribute to this upward trend. By uncovering the underlying mechanisms behind early-onset colon cancer, targeted prevention strategies and personalized treatment approaches can be developed.